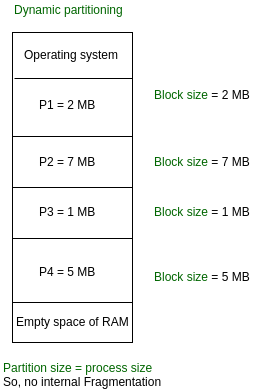
VARIABLE SIZE PARTITIONING
MVT
It is a part of Contiguous allocation technique. It is used to alleviate the problem faced by Fixed Partitioning. In contrast with fixed partitioning, partitions are not made before the execution or during system configure. Various features associated with variable Partitioning- Initially RAM is empty and partitions are made during the run-time according to process’s need instead of partitioning during system configure. The size of partition will be equal to incoming process. The partition size varies according to the need of the process so that the internal fragmentation can be avoided to ensure efficient utilisation of RAM. Number of partitions in RAM is not fixed and depends on the number of incoming process and Main Memory’s size.
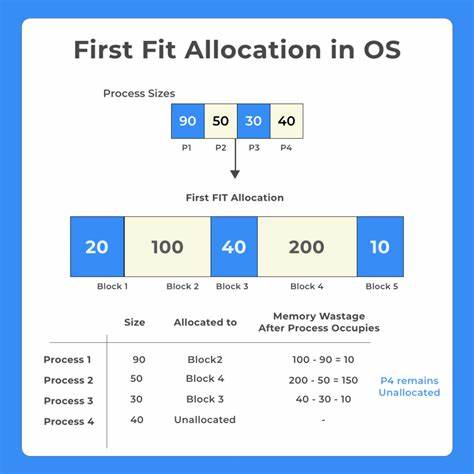
First Fit
This method keeps the free/busy list of jobs organized by memory location, low-ordered to high-ordered memory. In this method, first job claims the first available memory with space more than or equal to it’s size. The operating system doesn’t search for appropriate partition but just allocate the job to the nearest memory partition available with sufficient size.
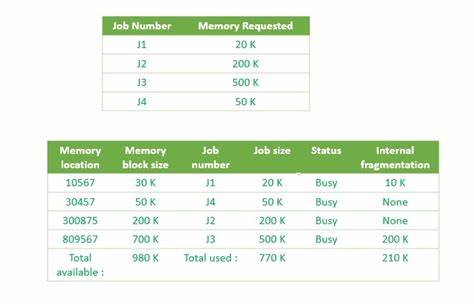
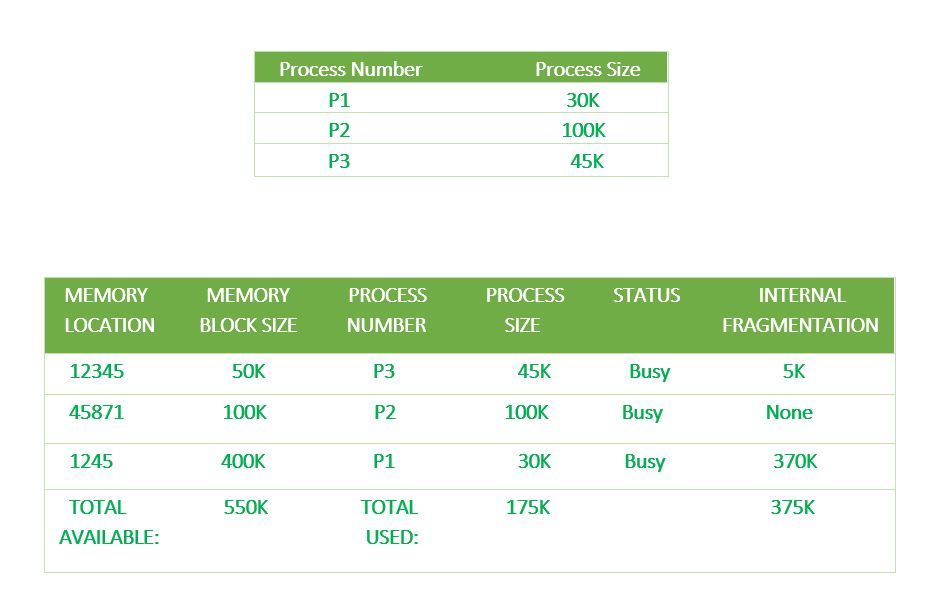
Best Fit
This method keeps the free/busy list in order by size – smallest to largest. In this method, the operating system first searches the whole of the memory according to the size of the given job and allocates it to the closest-fitting free partition in the memory, making it able to use memory efficiently. Here the jobs are in the order from smallest job to largest job.